- Home
- Flowering plants
- Petrea Racemosa (Purple Wreath, Queen’s Wreath, Tropical Wisteria)
Petrea Racemosa (Purple Wreath, Queen's Wreath, Tropical Wisteria)
Common names: Purple wreath, Queen’s wreath, Sandpaper vine, Fleur de Dieu, Nootka Cypress, Bluebird Vine, Tropical Wisteria, Fairy Lavender
usda zones
sunlight
Soil & water
fauna
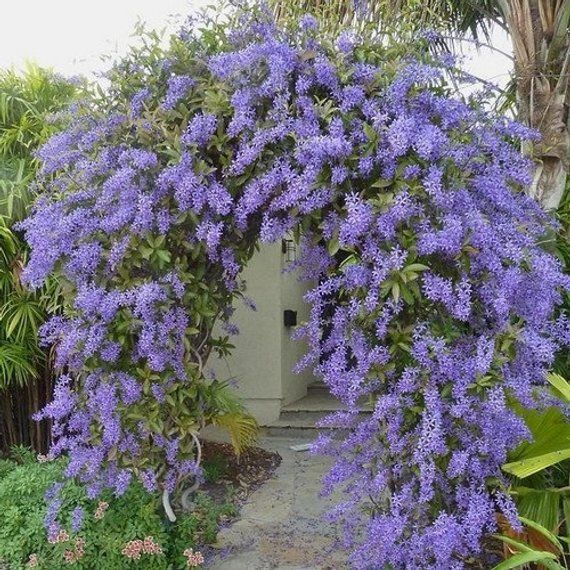
Description of Petrea Racemosa
Explore the allure of Petrea racemosa, available for sale to elevate your garden. Buy Petrea racemosa, a tropical climbing vine, to transform your outdoor space with its cascading clusters of vibrant, purple-hued flowers. This ornamental gem adds a touch of tropical elegance, making it a sought-after choice for landscaping enthusiasts.
Petrea racemosa, commonly known as Sandpaper Vine, emerges as a botanical masterpiece, capturing hearts with its distinctive charm and resilient nature. This unique tropical climbing vine, belonging to the Verbenaceae family, hails from Central America, notably Mexico and Guatemala. Its captivating features make it a coveted addition to gardens, where it flourishes as a testament to the wonders of nature.
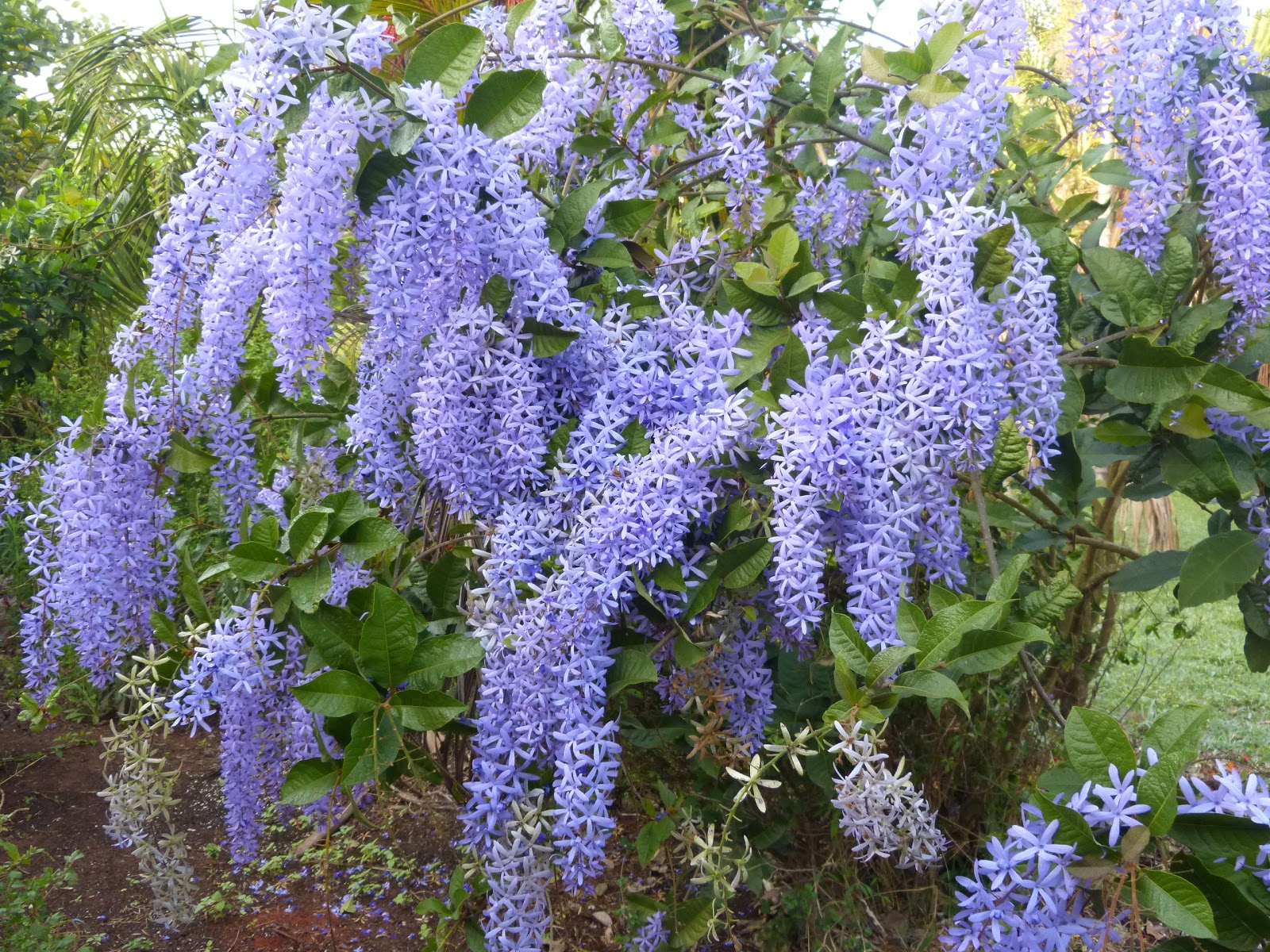
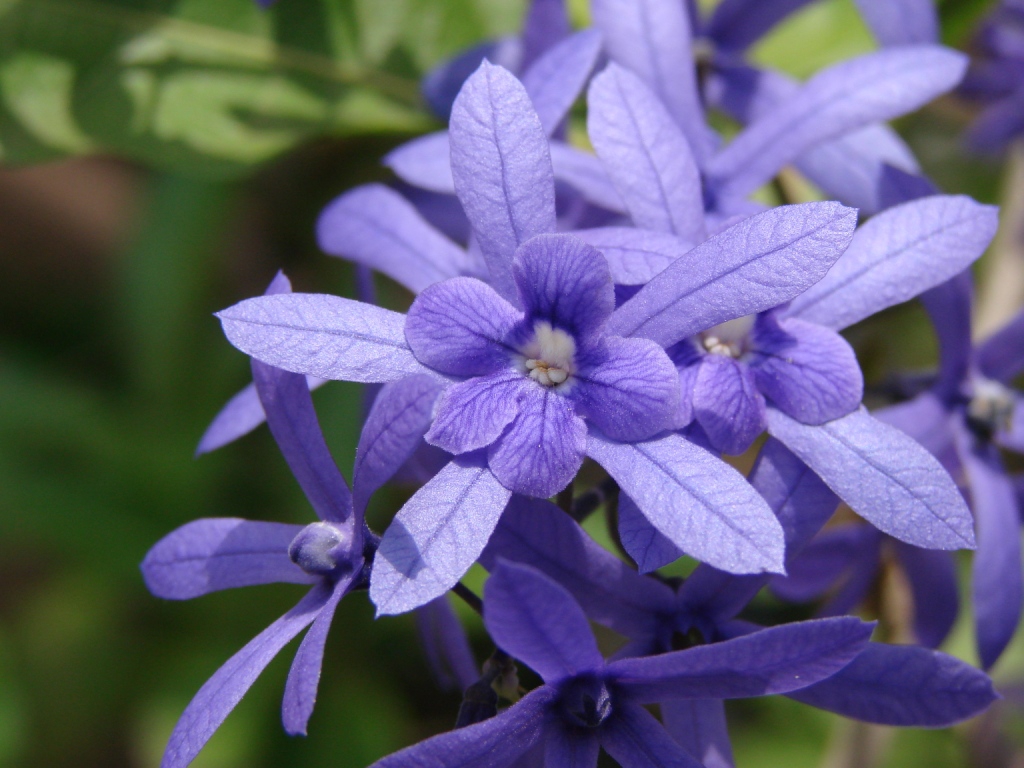
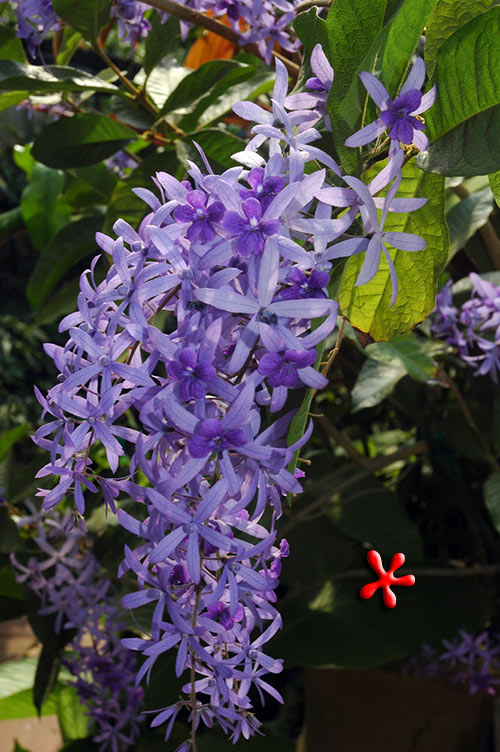
At the heart of Petrea racemosa’s allure lies its visual splendor. The plant boasts lustrous, deep green leaves characterized by a unique sandpaper-like texture, a tactile reminder of its botanical identity. These leaves form a verdant backdrop for the real showstopper – the cascading clusters of flowers. Each inflorescence is a symphony of lavender to violet-blue hues, creating an enchanting spectacle akin to a regal wreath. This elegant display has earned it the endearing nickname, “Queen’s Wreath.”
Petrea Racemosa VS. Wisteria
In a garden or landscape setting, the choice between Petrea volubilis and Wisteria depends on factors such as climate, space, and the desired aesthetic. Petrea volubilis brings a touch of the tropics with its textured leaves and year-round blooms, while Wisteria offers a burst of colors and fragrance during its distinct flowering season. Both vines contribute to the vertical beauty of outdoor spaces, each with its own allure and charm.
While both vines share a climbing habit and ornamental value, they differ in their botanical families, native regions, leaf textures, flower colors, and flowering times. Petrea volubilis boasts evergreen foliage and a continuous blooming pattern, while Wisteria has a specific flowering season. Additionally, the fragrance of their flowers varies, with Wisteria known for its potent scent.
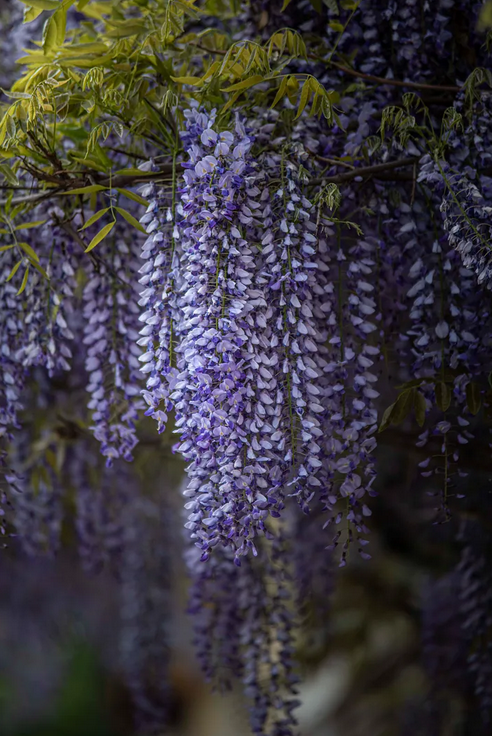

How to grow Petrea Racemosa
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to grow and care for this tropical climbing vine:
1. Climate and Hardiness:
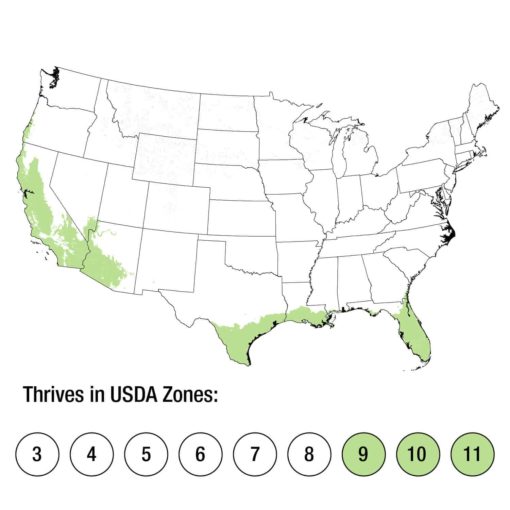
- Petrea racemosa thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. It is well-suited for USDA hardiness zones 9B-11. In cooler climates, it can be grown as a container plant and brought indoors during colder seasons.
2. Sunlight:
- Provide Petrea racemosa with bright, indirect sunlight. While it can tolerate some shade, exposure to ample light encourages abundant flowering and robust growth. For outdoor planting, choose a location with filtered sunlight or partial shade, especially in regions with intense afternoon sun.
3. Soil:
- Plant Petrea racemosa in well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. A rich, fertile soil with added organic matter is beneficial for optimal growth. While the vine can adapt to various soil types, a loamy, well-aerated mix is ideal.
4. Watering:
- Maintain a consistent watering schedule, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adjust the frequency based on factors such as temperature, humidity, and the plant’s growth stage. During the growing season, increase watering, and reduce it during the dormant period.
5. Temperature:
- Plant Sandpaper Vine in locations where temperatures remain within its preferred range. Protect it from frost and cold temperatures, especially in regions with occasional cold spells. Indoor cultivation is an option for areas with colder climates.
6. Support Structures:
- Given its climbing nature, provide support structures such as trellises or stakes. This is crucial for guiding the vine’s growth and preventing it from sprawling excessively. Ensure the support is sturdy and appropriate for the plant’s size.
7. Pruning:
- Regular pruning helps maintain the desired shape and size of Petrea racemosa. Trim yellow or damaged leaves, and prune to control growth. Pruning also promotes branching and fuller foliage. Perform pruning during the appropriate growing season.
8. Fertilizing:
- Fertilize Petrea racemosa during the active growing season with a balanced, all-purpose fertilizer. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for rates and application frequency. For best results use slow release fertilizer. It helps to avoid overfurtilizing and a chemical burn as a result.
9. Flowering and Fruit:
- Petrea racemosa produces cascading clusters of lavender to violet-blue flowers. These blooms emit a subtle, spicy fragrance, particularly in the evening. Pollinated flowers develop round fruits that turn orange when mature, adding an ornamental aspect to the plant. Note that the fruits are not edible.
10. Outdoor Planting Considerations:
- When planting outdoors, consider the upward and outward expansion of Petrea racemosa. Provide adequate space for its growth, and avoid overcrowding to ensure good air circulation.


Destinction between Petrea Racemosa vs. Petrea Volubilis
Petrea racemosa and Petrea volubilis are often confused due to their similar common names and appearances, but they are distinct species. Here are the key differences between these two species:
Common Names:
- Petrea racemosa is commonly known as Sandpaper Vine or Queen’s Wreath.
- Petrea volubilis is often referred to as Queen’s Wreath as well, contributing to the confusion. Additionally, it may be called Purple Wreath, Queen’s Wreath Vine, or even Sandpaper Vine.
Origin:
- Petrea racemosa is native to Central America, including regions such as Mexico and Guatemala.
- Petrea volubilis is native to Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America.
Flower Color:
- Petrea racemosa typically produces lavender to violet-blue flowers in cascading clusters, adding a vibrant touch to gardens.
- Petrea volubilis is known for its striking violet to purple flowers, often forming dense racemes that give it a wreath-like appearance.
Leaf and Flower Size:
- Both species share a characteristic of having rough or sandpapery leaves, contributing to their shared common name, “Sandpaper Vine.” Racemosa has significantly larger leaves and flowers.
Growth Habit:
- Petrea racemosa is a fast-growing, evergreen woody vine that can reach considerable heights with appropriate support.
- Petrea volubilis is also a vigorous, woody vine known for its rapid growth and climbing abilities.
Cultivation:
- Both plants thrive in tropical and subtropical climates, requiring warm temperatures and well-draining soil. They are suitable for outdoor cultivation in regions with appropriate climates.
While they share similarities, the distinct flower colors and native regions can help differentiate Petrea racemosa from Petrea volubilis.
Propagation Methods
Petrea racemosa’s propagation is best performed through hardwood / semi hardwood cuttings. This method is effective when aiming to replicate specific traits of a mature plant. This process is typically carried out in late summer, allowing the cuttings to establish roots over the fall and winter months.
1. Stem Cuttings:
- Select a healthy hardwood stem with a few leaves.
- Employ clean and sharp scissors or pruning shears to make a precise cut just below a node on the selected stem.
- Place the cutting in water or directly into soil, ensuring the node is submerged or buried.
- Wait for roots to develop before transplanting into a larger container.
Landscaping with Sandpaper Vine: Whether used as a standalone focal point or interwoven with other plants, Petrea racemosa elevates the aesthetics of any landscape. Its climbing habit allows it to gracefully drape over structures, creating a living tapestry of greenery and blossoms. Combining well with both tropical and subtropical plant companions, it offers endless possibilities for creative landscaping.
Fertilizing queen’s wreath
Fertilize Petrea Racemosa during the active growing season, which typically corresponds to spring and summer. These are the months when the plant is putting forth new growth and flowering.
Use a balanced, all-purpose fertilizer with equal or near-equal proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Alternatively, a fertilizer specifically formulated for flowering plants can be beneficial. Choose a slow-release granular fertilizer for a gradual nutrient release over time.







