- Home
- Evergreen Trees
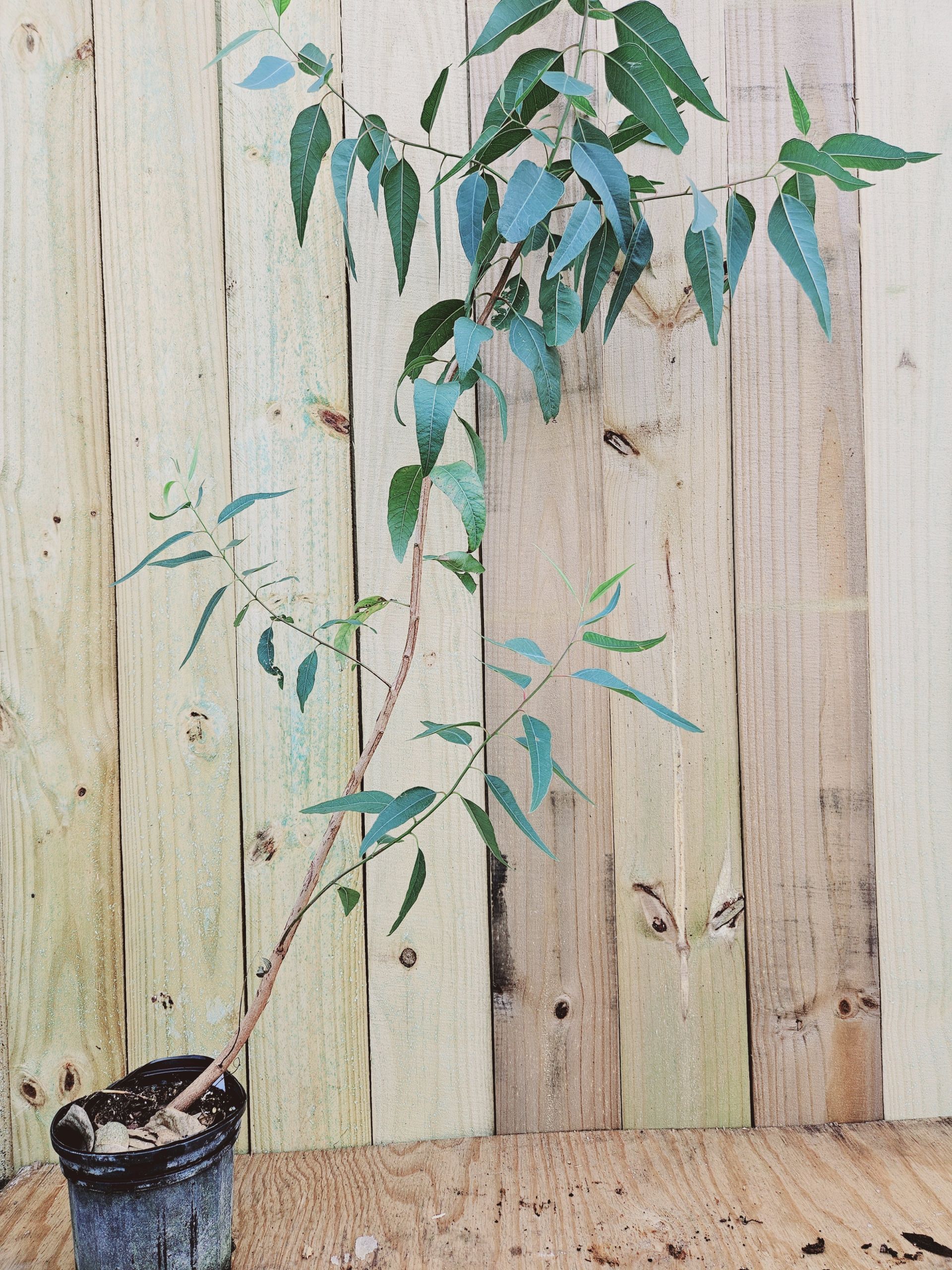
- Eucalyptus Teretecornis (Forest Red Gum, Blue Gum, Red Irongum) tree
Eucalyptus Teretecornis (Forest Red Gum, Blue Gum, Red Irongum) tree
Common names: Forest Red gum, Blue gum, Red irongum
Synonyms: Eucalyptus populifolia Desf
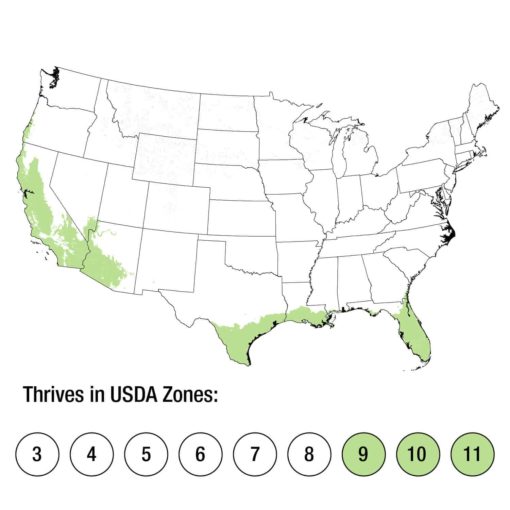
usda zones
sunlight
Soil & water
fauna
Description of Eucalyptus Populnea
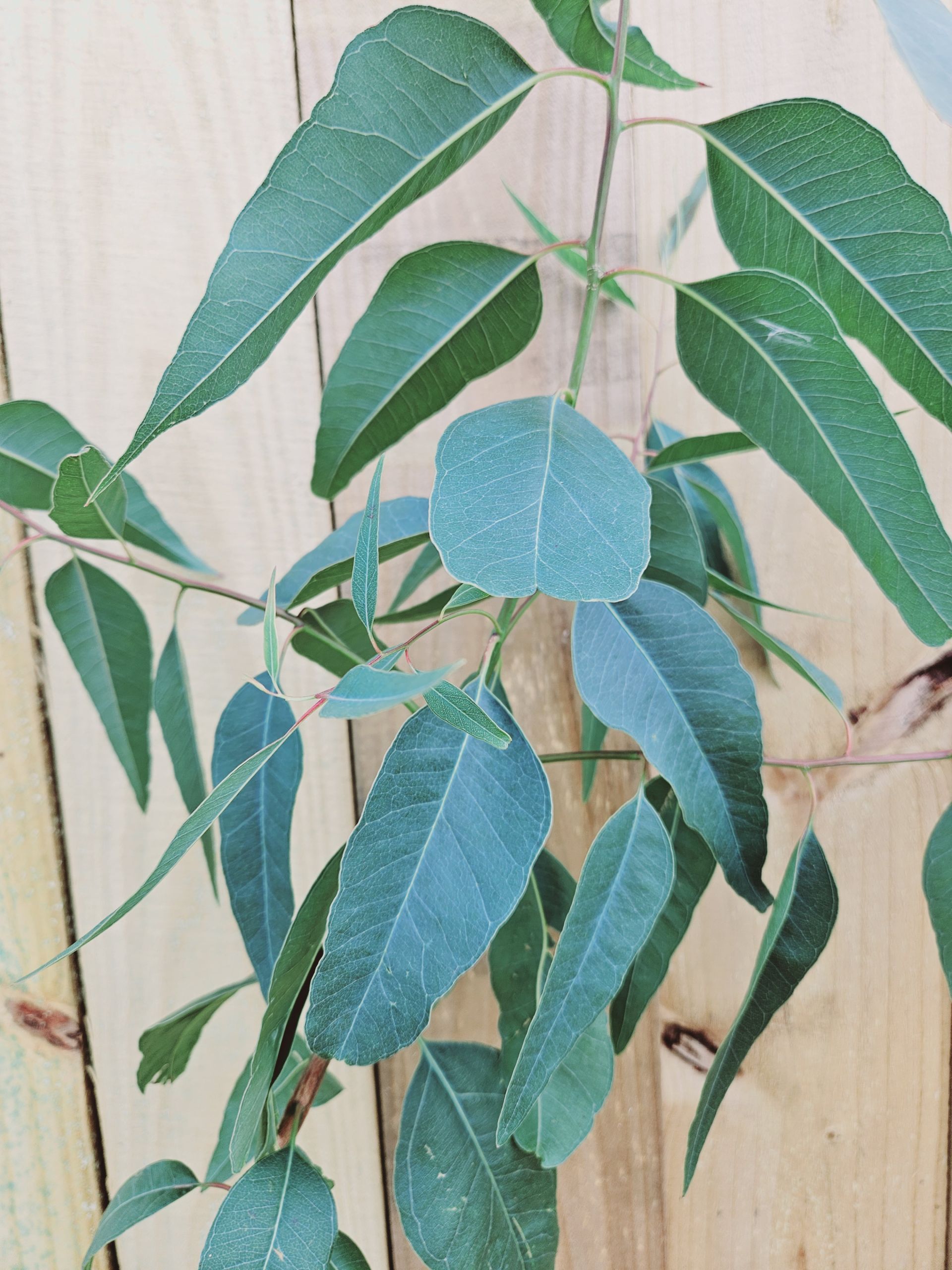
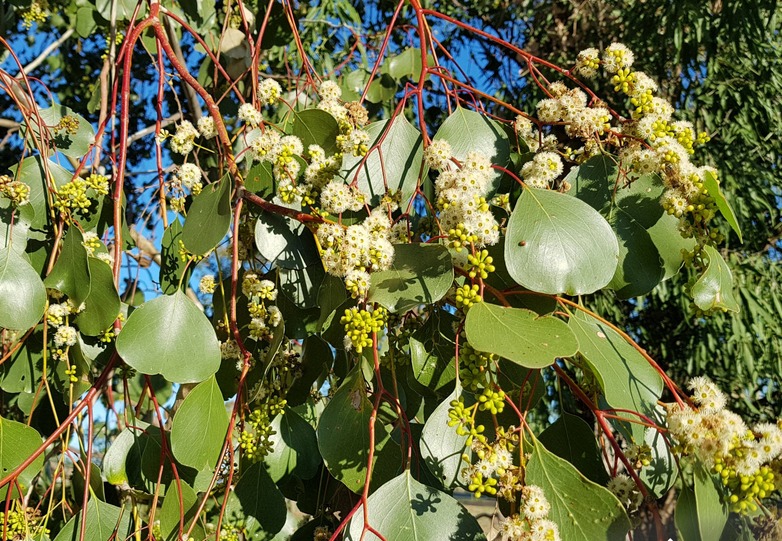
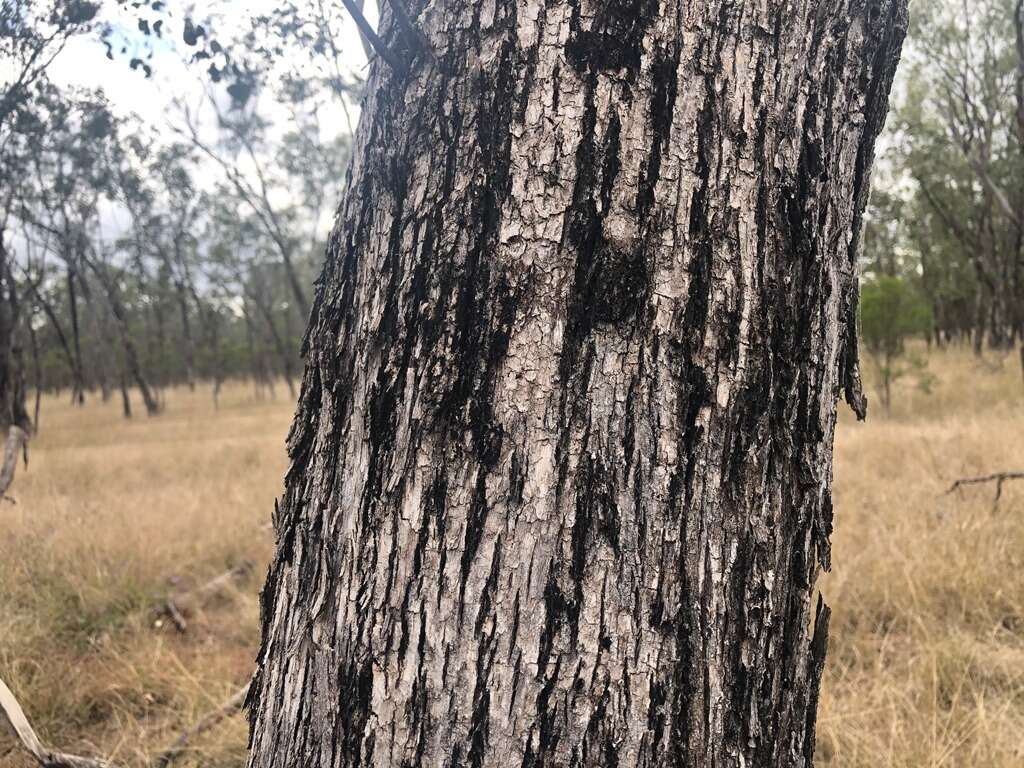
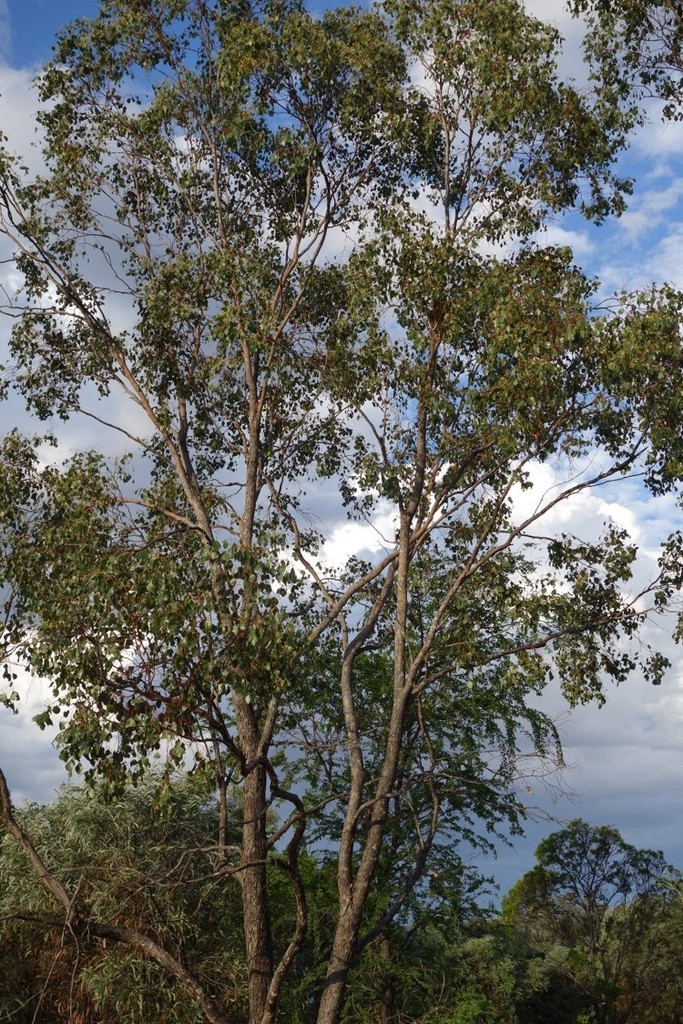
Eucalyptus populnea is a medium to large-sized tree that typically grows up to 15-25 meters (50-82 feet) tall, with a spreading canopy. Its bark is rough, fibrous, and persistent, often displaying shades of gray, brown, or reddish-brown. The trunk may have a mottled appearance due to shedding bark patches. The juvenile leaves are typically oval-shaped and bluish-green, while the adult leaves are more elongated and grayish-green.
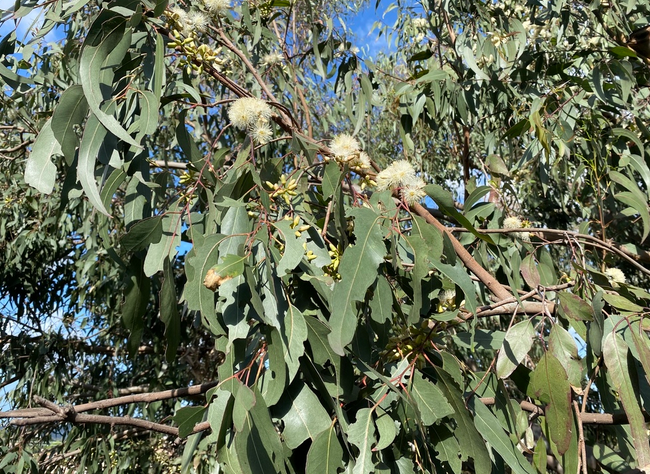
The tree produces clusters of small, creamy-white flowers, which bloom in spring or early summer. These flowers are highly attractive to bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Following flowering, woody capsules known as gum nuts develop, containing numerous small seeds. These capsules are an essential food source for various native birds and mammals.
Eucalyptus populnea is endemic to Australia, where it is primarily found in the eastern and central parts of the country. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including open woodlands, savannas, and forested areas. The tree is well-adapted to dry, arid conditions and is often found growing in regions with low rainfall and poor soils.
Medical and Cultural use
Indigenous Australian cultures have employed various parts of the Eucalyptus populnea tree for additional medicinal purposes. For example, decoctions made from the bark or leaves have been used to treat fevers, digestive disorders, and urinary tract infections. The aromatic smoke from burning eucalyptus leaves has been used in ceremonial rituals and as a natural insect repellent. (Low, 1990)
Research on the medicinal properties of Eucalyptus populnea has provided insights into its potential therapeutic and health benefits.
1. Respiratory Health:
- Eucalyptus populnea leaves contain volatile oils, including eucalyptol (1,8-cineole), which have expectorant and decongestant properties. Inhalation of steam infused with eucalyptus oil or drinking eucalyptus tea made from the leaves has been used to relieve symptoms of respiratory conditions such as coughs, colds, bronchitis, and asthma. These remedies help to loosen phlegm, soothe airways, and ease breathing. (Saeed Khalid et al., 2010)
2. Antimicrobial and Antiseptic Properties:
- The essential oils extracted from Eucalyptus populnea possess antimicrobial and antiseptic properties. They have been applied topically to treat minor wounds, cuts, and skin infections. Additionally, eucalyptus oil has been used as an ingredient in mouthwashes and gargles to help combat oral infections and promote oral hygiene. (Jirovetz et al., 2008)
3. Pain Relief:
- Eucalyptus oil derived from Eucalyptus populnea leaves contains compounds with analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. It has been used in topical preparations such as liniments, ointments, and massage oils to alleviate muscular aches, joint pain, and headaches. The application of eucalyptus oil to the affected area may help reduce inflammation and provide relief from discomfort. (Silva et al., 2017)
4. Antioxidant Effects:
- Some studies suggest that extracts from Eucalyptus populnea leaves may exhibit antioxidant activity due to the presence of phenolic compounds. Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage and potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer. (Weli et al., 2007)


How to grow Eucalyptus Populnea
Growing Eucalyptus Populnea, also known as Bimble Box or Poplar Box, requires attention to its specific needs. Here’s a guide on how to grow this tree:
1. Climate and Location:
- Eucalyptus Populnea thrives in warm, temperate climates and is well-suited to regions with hot, dry summers and mild winters (USDA Zones 9-12). Choose a planting location that receives full sunlight for optimal growth.
2. Soil Requirements:
- Plant Eucalyptus Populnea in well-draining soil with good aeration. While it can tolerate a range of soil types, including sandy or loamy soils, it prefers slightly acidic to neutral pH levels. Avoid waterlogged or compacted soils, as these can lead to root rot.
3. Watering:
- Initially, water newly planted trees regularly to establish a strong root system. Once established, Eucalyptus Populnea is drought-tolerant and requires minimal watering. Allow the soil to dry out between waterings to prevent overwatering, which can be detrimental to the tree’s health.
4. Propagation:
- Eucalyptus Populnea can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. Collect seeds from mature gum nuts and sow them in trays filled with seed-raising mix. Keep the soil moist and provide warmth and sunlight for germination. Alternatively, take hardwood cuttings from healthy, mature trees and root them in a well-draining propagation mix.
5. Pruning:
- Pruning is best done during the tree’s dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring, using sharp, clean pruning shears or loppers for smaller branches and a pruning saw for larger ones. Start by removing dead, damaged, or diseased branches, then thin out overcrowded areas of the canopy to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration. Shape the tree by selectively removing branches growing in undesirable directions, but avoid topping, which can lead to weak growth. Prune regularly to control size, encourage bushier growth, and maintain a specific height if desired.
6. Fertilization:
- Eucalyptus Populnea is relatively low-maintenance and typically does not require fertilization in its native habitat. However, if growing in poor soil or as part of a landscape planting, a balanced fertilizer applied in spring can help promote growth. Avoid excessive fertilization, as this can lead to nutrient imbalances. Use slow release fertilizer for best results.
7. Mulching:
- Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Keep the mulch several inches away from the trunk to prevent moisture-related issues and discourage pests and diseases.
8. Pest and Disease Management:
- Eucalyptus Populnea is generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, monitor the tree for signs of pest infestations, such as leaf-chewing insects or borers, and treat as necessary with appropriate insecticides or cultural controls. Ensure good air circulation around the tree to prevent fungal diseases.
- Rhizactonia Root and Stem Rot is a fungus that is found in most soils and enters the plant through the roots or the stem at soil level.
Prevention and Control: First of all, do not overwater and if you suspect Rhizoctonia may be your problem, decrease watering. If a plant is too far gone (all the leaves from the bottom up are wilted), remove it. If your plant is in a container, discard the soil too. Wash the pot with a 1 part bleach to 9 parts water solution. Fungicides can be used, according to label directions. Consult a professional for a legal recommendation of what fungicide to use.
-
Fungi : Powdery Mildew is usually found on plants that do not have enough air circulation or adequate light. Problems are worse where nights are cool and days are warm and humid. The powdery white or gray fungus is usually found on the upper surface of leaves or fruit. Leaves will often turn yellow or brown, curl up, and drop off. New foliage emerges crinkled and distorted. Fruit will be dwarfed and often drops early.
Prevention and Control: Plant resistant varieties and space plants properly so they receive adequate light and air circulation. Always water from below, keeping water off the foliage. This is paramount for roses. Go easy on the nitrogen fertilizer. Apply fungicides according to label directions before problem becomes severe and follow directions exactly, not missing any required treatments. Sanitation is a must – clean up and remove all leaves, flowers, or debris in the fall and destroy. - Pythium and Phytophtora Root Rot occurs when soil moisture levels are excessively high and fungal spores present in the soil, come in contact with the susceptible plant. The base of stems discolor and shrink, and leaves further up the stalk wilt and die. Leaves near base are affected first. The roots will turn black and rot or break. This fungi can be introduced by using unsterilized soil mix or contaminated water.
Prevention and Control: Remove affected plants and their roots, and discard surrounding soil. Replace with plants that are not susceptible, and only use fresh, sterilized soil mix. Hold back on fertilizing too. Try not to over water plants and make sure that soil is well drained prior to planting. This fungus is not treatable by chemicals.Rhizoctonia Root and Stem Rot symptoms look similar to Pythium Root Rot, but the Rhizoctonia fungus seems to thrive in well drained soils.
- Pest : Aphids are small, soft-bodied, slow-moving insects that suck fluids from plants. They come in many colors, ranging from green to brown to black, and they may have wings. They attack a wide range of plant species causing stunting, deformed leaves and buds. They can transmit harmful plant viruses with their piercing/sucking mouthparts. Aphids, generally, are merely a nuisance, since it takes many of them to cause serious plant damage. However aphids do produce a sweet substance called honeydew (coveted by ants) which can lead to an unattractive black surface growth called sooty mold.
Aphids can increase quickly in numbers and each female can produce up to 250 live nymphs in the course of a month without mating. Aphids often appear when the environment changes – spring & fall. They’re often massed at the tips of branches feeding on succulent tissue. Aphids are attracted to the color yellow and will often hitchhike on yellow clothing.
Prevention and Control: Keep weeds to an absolute minimum, especially around desirable plants. On edibles, wash off infected area of plant. Lady bugs and lacewings will feed on aphids in the garden. There are various products – organic and inorganic – that can be used to control aphids. Seek the recommendation of a professional and follow all label procedures to a tee.
Do Eucalyptus TREES grow fast
Like many eucalyptus species, Eucalyptus Populnea is a fast growing tree, particularly when provided with adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients.
In optimal growing conditions, Eucalyptus Populnea trees can exhibit rapid growth, adding 6 to 10 feet in height in a single growing season, often reaching mature heights within a relatively short period compared to many other tree species. However, the exact growth rate of Eucalyptus Populnea can vary depending on factors such as soil quality, water availability, temperature, and sunlight exposure.
Do not plant the tree under electrical wires or very close to buildings.
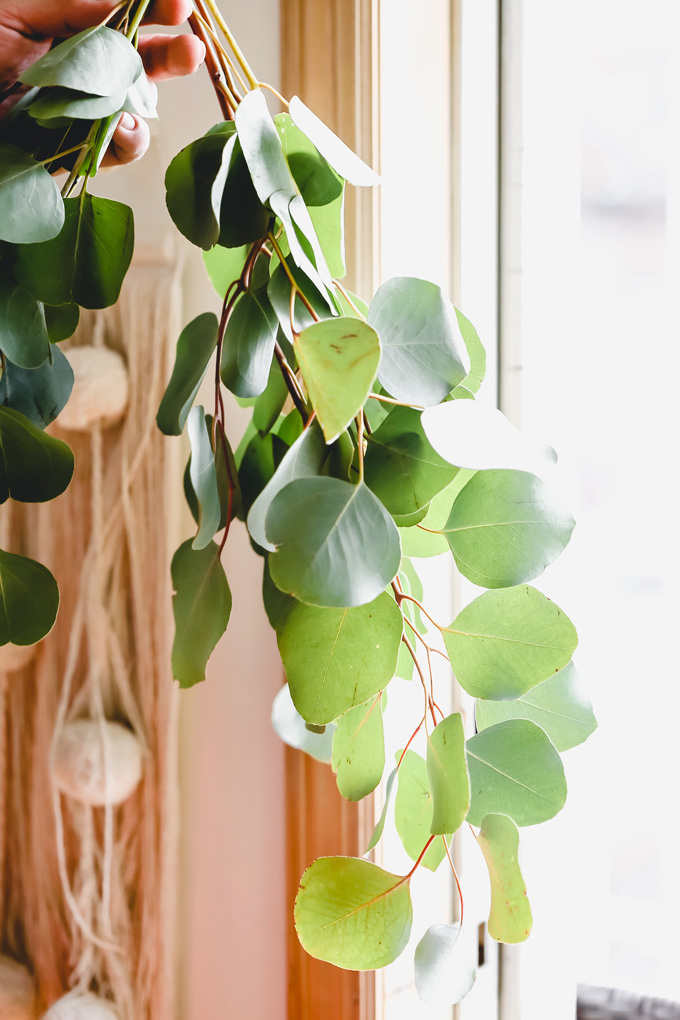


The Benefits Of Hanging Eucalyptus In Your Shower
Hanging eucalyptus branches in the shower provides a plethora of benefits.
Firstly, the steam from the shower releases the aromatic oils present in eucalyptus leaves, filling the air with a refreshing, invigorating scent. This natural fragrance can help uplift the mood, promote relaxation, and alleviate stress.
Additionally, eucalyptus contains compounds such as eucalyptol that have decongestant and expectorant properties, making it effective in clearing nasal passages and relieving sinus congestion.
Moreover, eucalyptus oil has anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe muscle aches and pains, while also promoting skin health by cleansing and preventing bacterial growth.
Lastly, the invigorating scent of eucalyptus can enhance mental clarity, improve focus, and provide a sense of refreshment and rejuvenation, making it an excellent addition to your daily routine.






